Chiropractic was founded in 1895 after a spinal adjustment to the upper region of the spine restored a man's hearing.
Since then, our profession has been conducting research to help determine why spinal manipulation or adjustments work so well.
Many conditions have been studied, as well as the physiological responses to the adjustment including changes to blood chemistry and hormone levels, blood pressure, circulation, and many other parameters of health.
Posture, bone alignment, and spinal curves have been long been evaluated in patients presenting with muscle and joint complaints by most of the healthcare professions, including chiropractic.
But the question remains: how important are spinal curves in the overall health picture of the patient? Can alterations in the "normal" curve lead to future trouble or be the cause of a current condition?
One study reviewed 54 studies published between 1942 and 2008, which included over 20,000 patients, and reported an association between the sagittal curve (curves when looking at a person from the side) and various health conditions.
There were many different types of studies and methods used to evaluate the sagittal curves of the lumbar (low back) (38 studies), thoracic (mid back) (34 studies) and cervical (neck) (6 studies) spine. These methods included plain x-ray (25 studies), MRI (1 study), photographs (3 studies) visual analysis or, by the eye (5 studies) and those using a variety of instruments (21 studies).
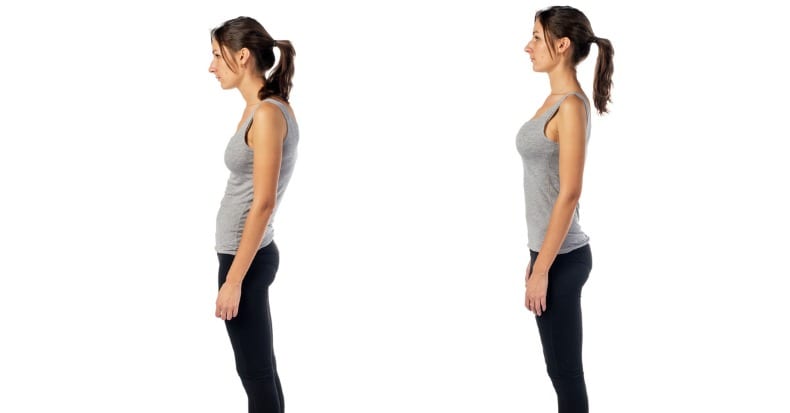
A strong association was reported in five studies with an increased angle in the midback/thoracic spine (kyphosis - sometimes referred to as "humpback") with lung disorders causing breathing problems. Poor physical function and pelvic organ prolapse were also strongly associated with kyphosis. Similarly, future osteoporotic midback/thoracic compression fractures were moderately associated with kyphosis or "humpback" deformity. Kyphosis was also moderately associated with heavy household activity, uterine prolapsed and death in three other studies.
A moderate association was found when the low back curve (lordosis) was reduced, which was associated with an increase in low back pain.